Technology & Services
Recent News
-
ESWL treatment of kidney stones nursing
1. bladder irritation Care Bladder irritation catheter is placed after the most common clinical symptoms. Patients complaining of abdominal discomfort and urinary frequency , urgency, dysuria and other . The reason may be placed catheter d...
2022-10-06
QBF
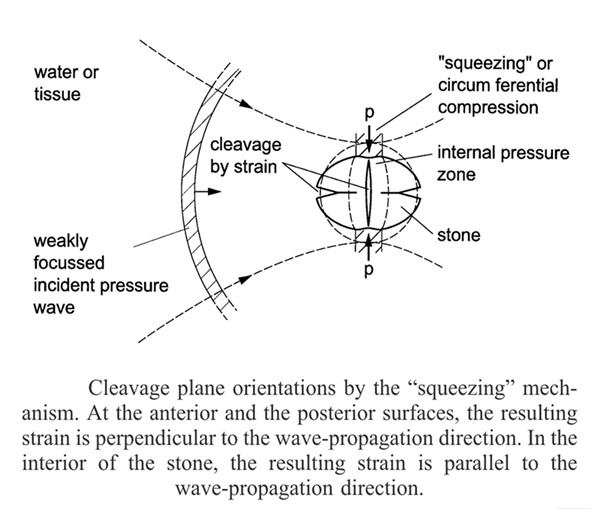
With focus diameters of the order of the stone dimension or larger, fragmentation in planes perpendicular and parallel to the wave plane is observed. This is explained by circumferential pressure or "squeezing" of the stone by the wave propagating at the outside of the stone in the liquid or tissue. Since the pressure zone propagates with the sound velocity in the liquid which is below the propagation velocity in the stone, it causes an evanescent pressure zone in the stone resulting in tensile stress in planes perpendicular and parallel to the wave plane.Under the stroke of wave again and again,the stone was broken into two,then four,then eight...the number increased at the geometrical rate. A quantitative model predicting the ratio of pulses needed to fragment the stone to 2 mm particle size in relation to the number of pressure pulses needed for the first fragmentation is well in accord with experiments, supporting the "squeezing mechanism with binary fragmentation". On the basis of these results it appears now possible to optimize the pressure pulse parameters which can be determined with high precision by measurements with the Fiber Optic Probe Hydrophone FOPH developed at the University of Stuttgart.
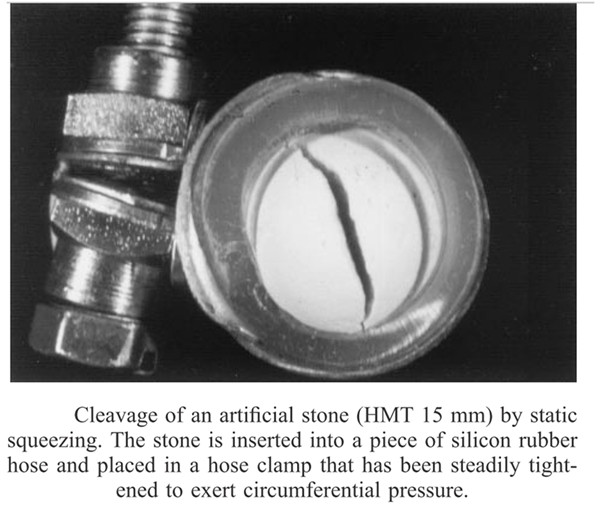

Fragmentation results for artificial stones (HMT 15mm diameter) with increasing number of shock waves. Thepulse pressure was 25 MPa, with 1-µs pulse duration and a2 6-dB focal diameter of 22 mm. The figure shows, from left toright, first the stone, then fragmentation after 7 pulses, 60pulses, 120 pulses and 500 pulses, with particle size below 2mm. The results were obtained using a separate stone for eachfragmentation.